Modeling
General information about Modeling in Renga
To work with a model, Renga provides a set of tools in 3D and 2D level views, commands to manage objects, and snap and measure modes for accurate construction.
Dimensions, that were specified during a building construction, correspond with the real building sizes.
The principles of work with tools are the same on both 3D and 2D views. In order to display the 2D view, open the level's plan.
Objects in 2D views are displayed as projections or sections, depending on the section plane location . To display all objects in the level view as thin lines, disable the Display true line thickness option in Settings.
The Level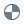 tool is available on the 3D view only.
tool is available on the 3D view only.
In Renga the objects with identical types can be overlapped, i.e. it is allowed to build an object over the other one if their types are the same.
When objects of different types intersect, one object cuts out the volume from the other, according to the following cutting priority:
|
↓ |
|
↓ |
|
↓ |
|
↓ |
|
↓ |
|
↓ |
|
↓ |
The Roof, Stairs, and Ramp are not cut out the volume, but cut off the volume that is located above them from the objects that are lower in priority.
And more:
- Window and Door cut the Wall volume, forming openings in the walls.
- Opening cuts the Floor and Roof volume.
- Hole cuts the Wall, Beam, Column, Floor, Roof, Isolated foundation and Wall foundation volume.
Cuts, openings, and holes change object quantities.
Parameters, properties and quantities of objects, specified or obtained during modeling, can be used when creating schedules and legends, when creating tag styles, in filters, as well as when exporting to CSV and IFC formats.
Read about all Renga modeling tools in the following topics:
Tips
When building objects that are built at more than one point, the mouse pointer shows which point will be set next, depending on the selected construction method. For example, in the construction of Arc wall by specifying three points, the pointer changes as follows: 

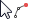 .
.
If an object can't be built in the specified point, the pointer is displayed as follows: 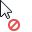 . For example, windows and doors can only be built in walls, pipe on a route, and wiring accessories on walls, beams, columns or floors if the measure mode is Cubic, Cylindrical or Spherical.
. For example, windows and doors can only be built in walls, pipe on a route, and wiring accessories on walls, beams, columns or floors if the measure mode is Cubic, Cylindrical or Spherical.
If it is not possible to build an object, such as a pipe on a route, a sign will be displayed notifying that the object cannot be built:  . This means that the object must be edited using handles or its style must be changed.
. This means that the object must be edited using handles or its style must be changed.